Friends, I wanted to teach pattern programs from Java Loops. But most people don't know much about loops. They just remember the loops and after a while forget the steps of the loops in them. You should read this post thoroughly, only then the problems in your for-each loop will disappear and you will become an expert.
- Java Do While Loop with Simple Example
- Java While Loop with Simple Example
- Java For Loop with Simple Example
Even if you don't know about this for-each loop, you can get complete information by reading the post. Here you will learn how to do Dry-Run.
Java Loop Overview
The concept of loops is very old in programming. If you have learned c and c ++, you have seen different loops in them too. The only difference is that, with the slightest change in the concept of loops, new loops came in the latest programming languages.
In programming, the loops concept is included in the control statement. This includes more if-else statements, break statements, continue statements. The goto statement has been removed from java. Control statements are used to change the flow of a program or to achieve something.
What is a loop in java?
Looping in programming languages is a feature that facilitates the execution of a set of instructions/functions repeatedly while some condition evaluates to true.
Types of loops in java?
In Java, there are four kinds of loops which are – the for loop, the while loop, the do-while loop, and the for-each loop. All these four-loop constructs of Java execute a set of repeated statements as long as a specified condition remains true. This particular condition is generally known as loop control.
In this post, you will only see the for-each loop with a simple example. The next post will contain information about the Nested loops with examples. As well as. You can learn the java-do-while loop by clicking here.
4 Easy Ways to Become an Expert in Java Loops?
- To know the syntax of loops.
- Understanding the flow of the loop.
- To do Dry Run.
- To practice.
I am going to teach these four options below. Read everything carefully and practice. Comment if you have any problems.
Java For-each Loop Overview
This for-each loop is specifically designed to handle the elements of a collection. The collection represents a group of elements. For example, we can take an array as a collection or any class in java.util package can be considered as a collection. The reason is that an array stores a group of elements like integer values or strings. Similarly, java.util package classes are developed to handle a group of objects.
The for-each loop repeatedly executes a group of statements for each element of the collection. It executes as many times as there is a number of elements in the collection.
Syntax of a for-each loop in java
for(var : collection ){statements;}
Here, var is attached to the collection. This var represents each element of the collection one by one. Suppose, the collection has got 5 elements then this loop will be executed 5 times, and the var will represent this one by one.
What are the 2 steps in Java for-each loop?
For-each Loop has 2 steps, the loops are made up of steps. The structure of the steps in each loop is different. Next, we will see the design of the for-each loop with an example.
1. Variable Initialization (Expression 1):
You have to write a variable, which stores one by one value in an array or collection When the loop is executed.
2. Statements:
When your loop starts, all the operations you want to do have to be written in the statement block. We will see that in the next example.
.
Java For-each Loop with Simple Example
To understand the preceding syntax, let us take an example.
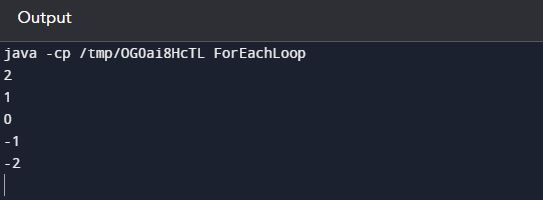
class ForEachLoop{public static void main(String[] args){//declare an array with 5 elementsint[] arr = {2,1,0,-1,-2};//use for-each loop to retrive elements from arrayfor( int i : arr){//i represents each element of arraySystem.out.println(i);}}}
In for-each loop no need to do a dry run. Here we are passing a group of elements and this loop internally stores a value one by one in the variable. In it, you can't any type of change. Because of that, there is no need to do dry-run. You can do it on other loops
Java For-each Loop Examples for Practice
Now your Java For-each Loop problem will be solved. If there is still any problem, read the post carefully.
Now you want to practice For-each Loop. Here are some For-each Loop examples, you want to solve. Many of these examples also ask the interviewer. Download the following file for its solution.
- Write a program, to take an array with 10 integer elements, print each element using for-each loop.
- Write a program, to take an array with 12 String elements, Elements are the 12 Months of the year. print each month name using for-each loop.
- Download Popular PC Games

Post a Comment